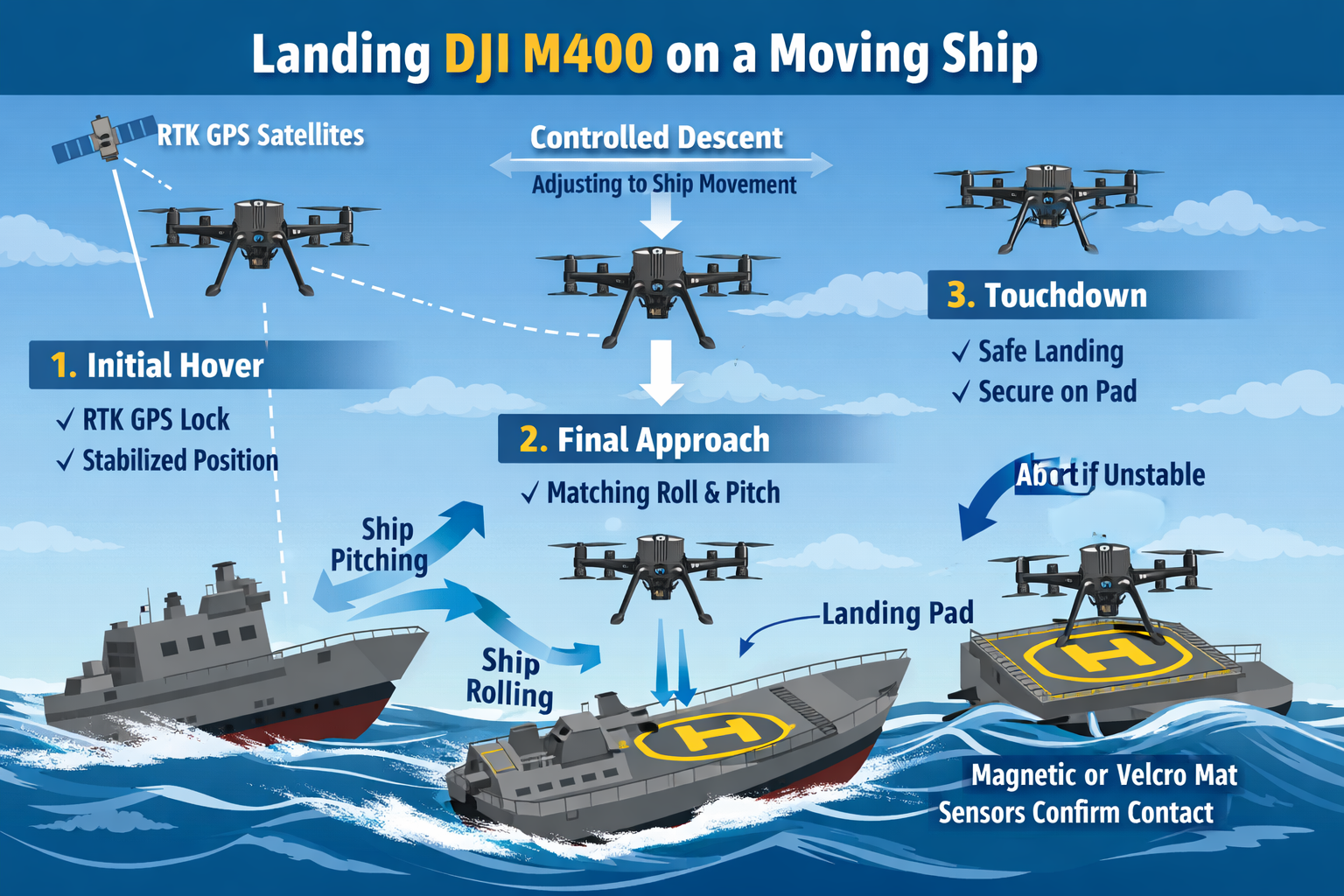
Step 1 – Prepare Landing Zone
Mark a dedicated landing pad with a high-visibility “H”. Ensure the area is clear of obstructions and fitted with an anti-slip or magnetic surface. Bridge and deck crew should stabilize the area and reduce ship speed where possible.
Step 2 – Pre-Landing Positioning
Hover while maintaining GPS/RTK lock. Establish an intermediate hover point 10–15 m above the pad. IMU and barometer compensate for wave-induced vertical motion.
Step 3 – Match Ship Motion
The flight controller tracks deck movement using GPS and downward sensors, continuously adjusting roll, pitch, and yaw to remain aligned with the moving vessel.
Step 4 – Descent & Final Approach
Begin slow descent (< 0.5 m/s). Downward vision, infrared, or optical flow sensors identify the pad. Pilot manually compensates for wind or sudden deck movement.
Step 5 – Touchdown
Landing legs absorb impact. Contact sensors confirm touchdown and motors reduce power gradually. Active braking prevents sliding on wet or sloped decks.
Step 6 – Secure Drone
Tether or magnetically secure the aircraft. Verify battery status and fully shut down motors.
Step 7 – Contingency Handling
- Abort landing and climb to hover altitude
- Wait for deck stabilization
- Maintain manual override at all times
Key Technologies
- RTK GPS / GNSS (cm-level accuracy)
- Downward vision & obstacle sensing
- IMU-driven stabilization algorithms
- Manual pilot control
✅ Operational Summary
Shipboard recovery of the DJI M400 is a coordinated balance of sensor fusion and pilot skill. Slow descent, stabilized pad, and immediate abort capability are essential for safe operations while the vessel is underway.